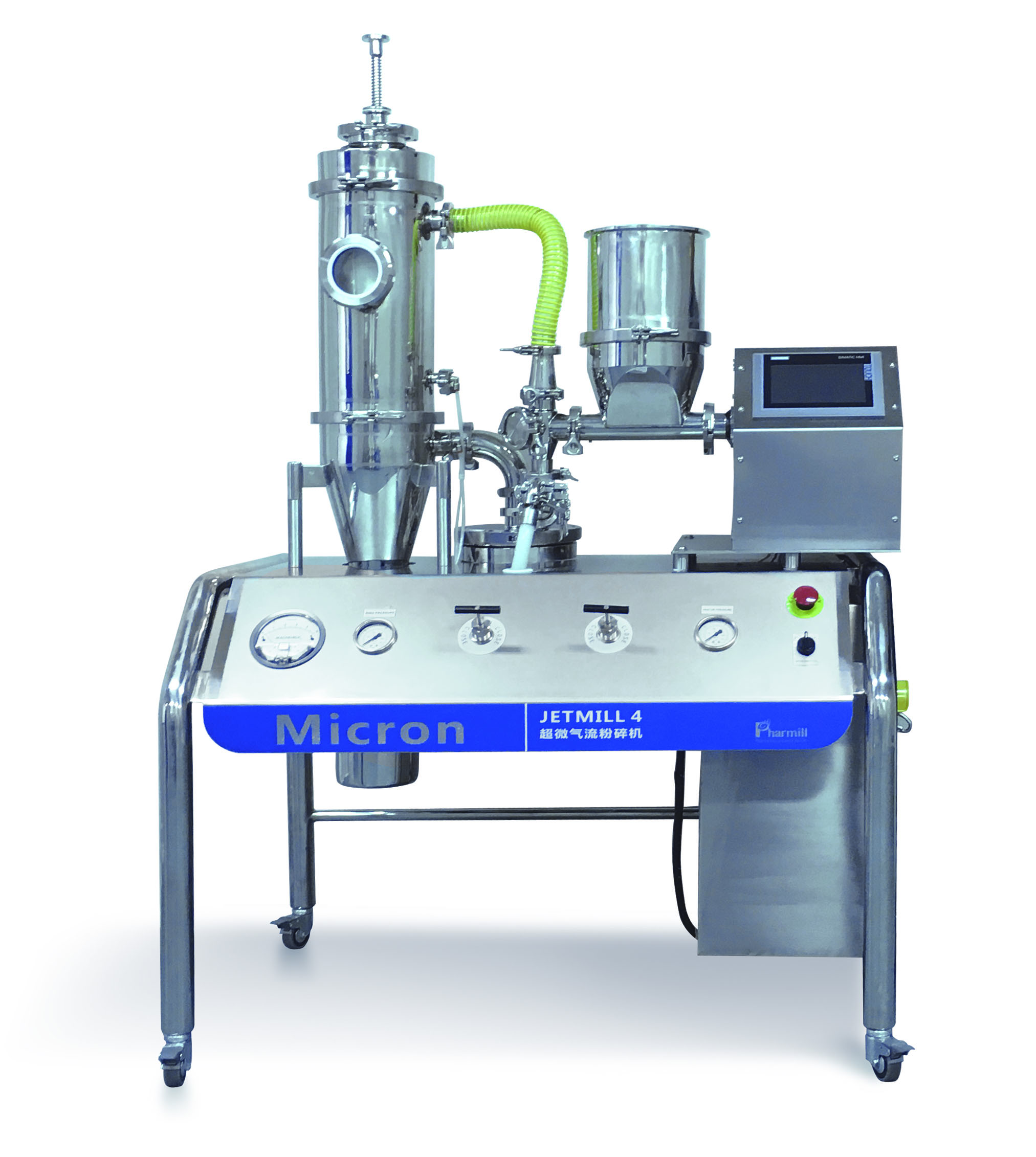
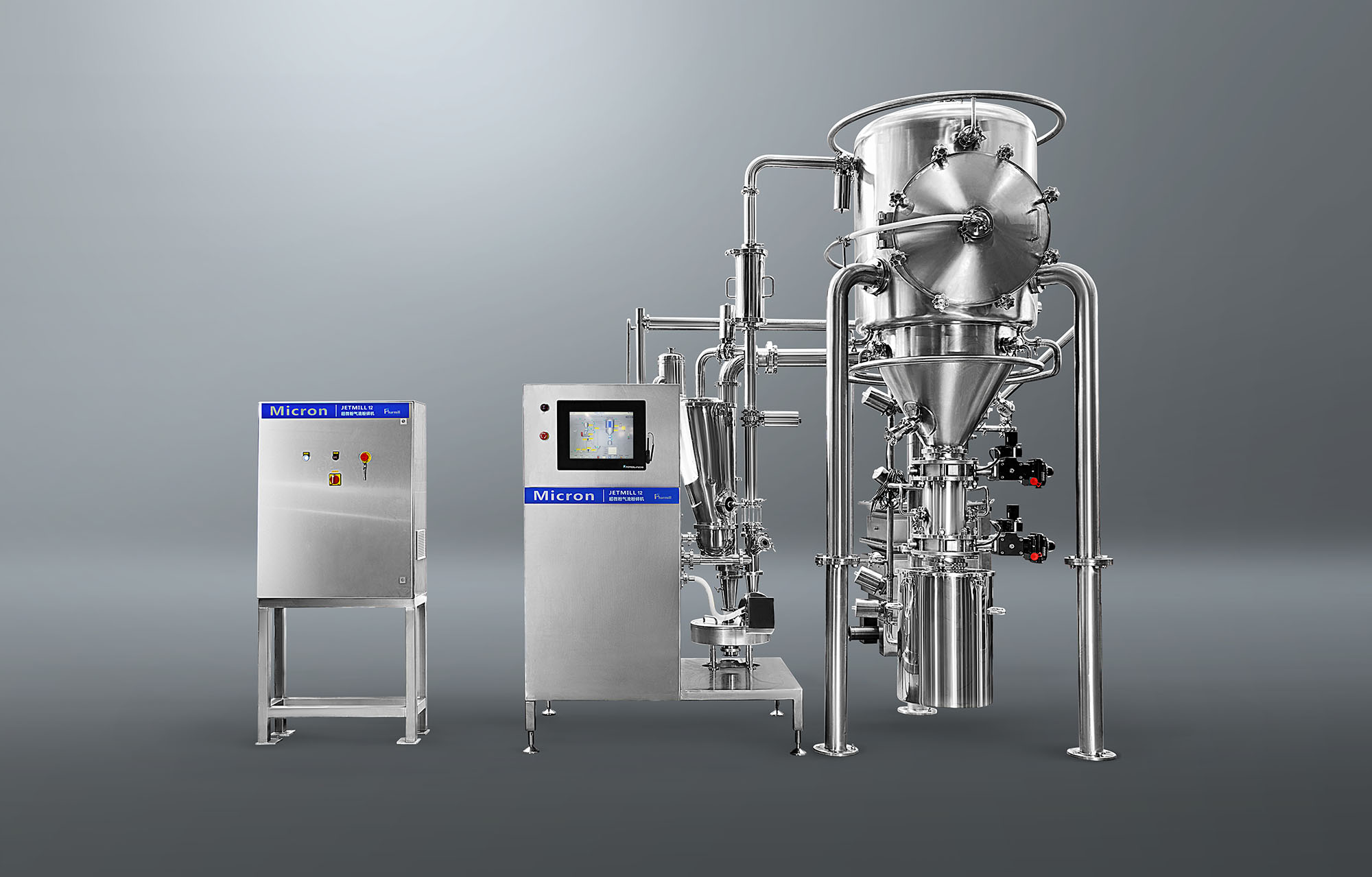
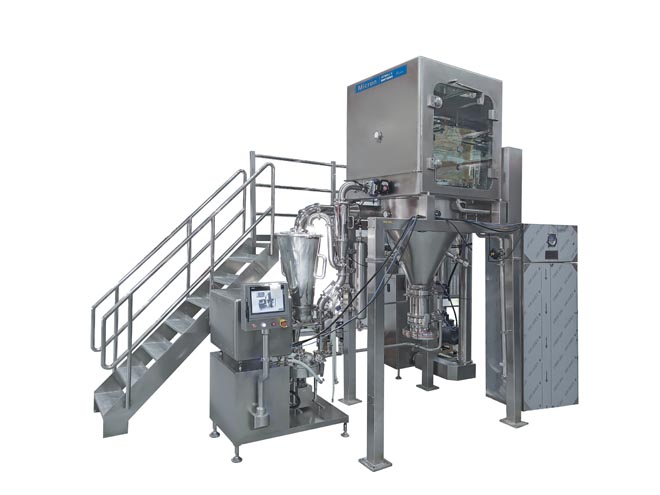
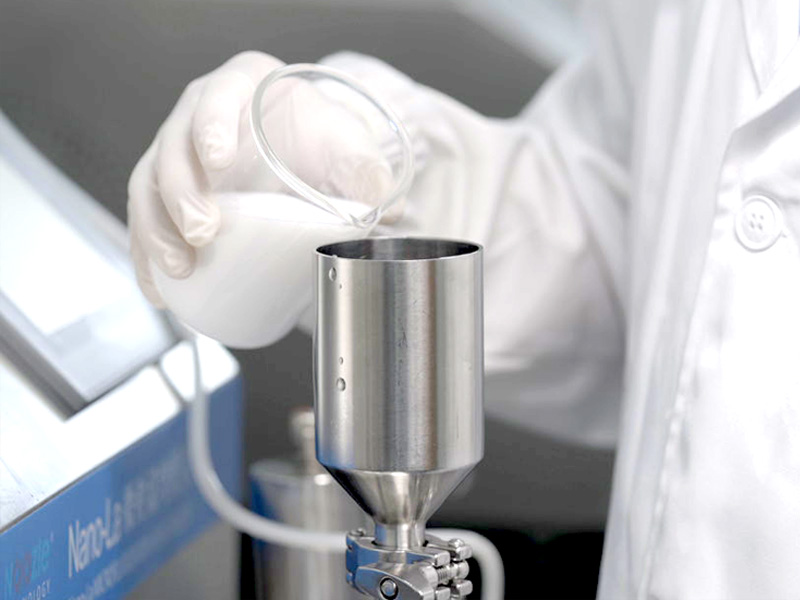
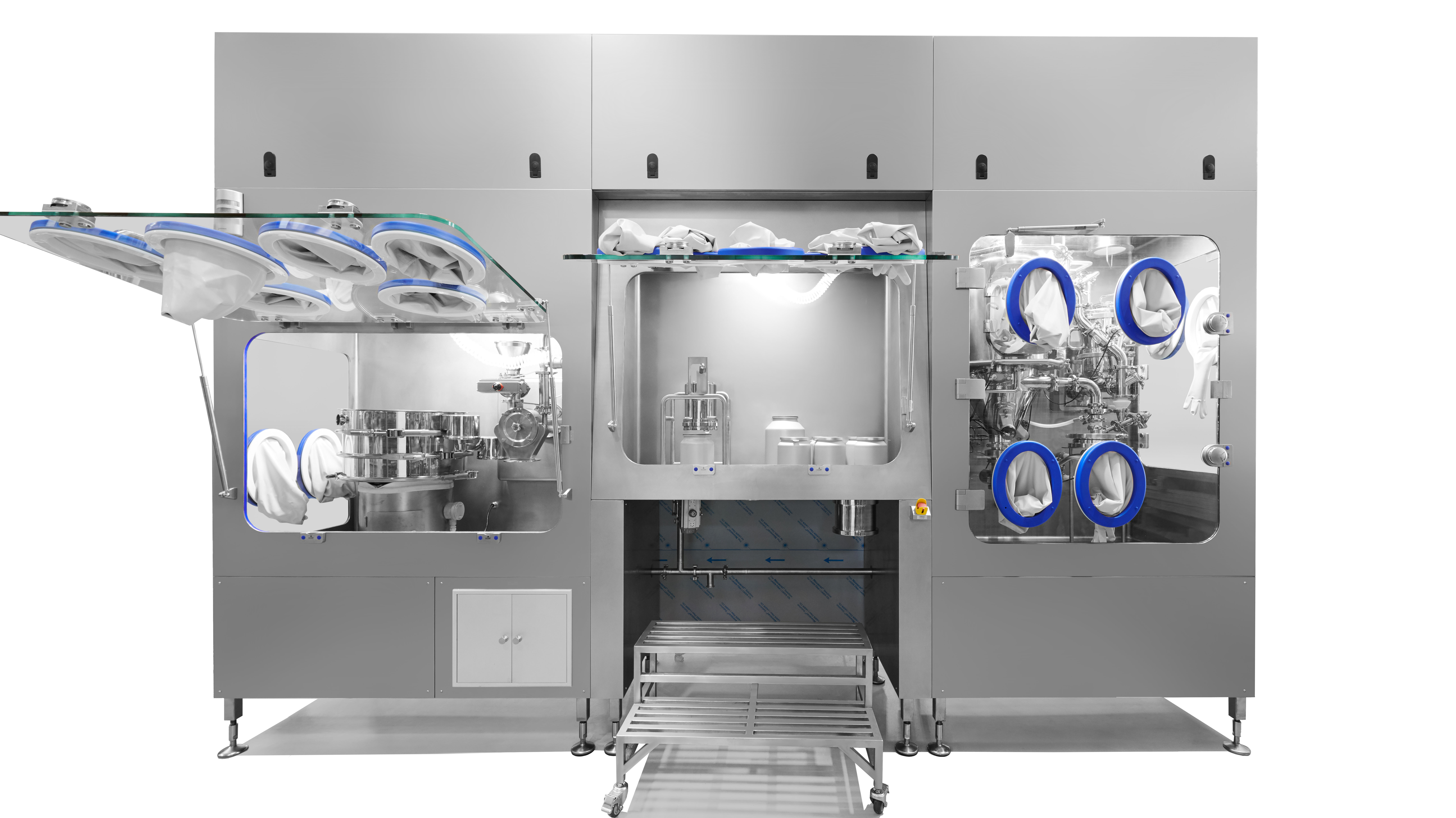
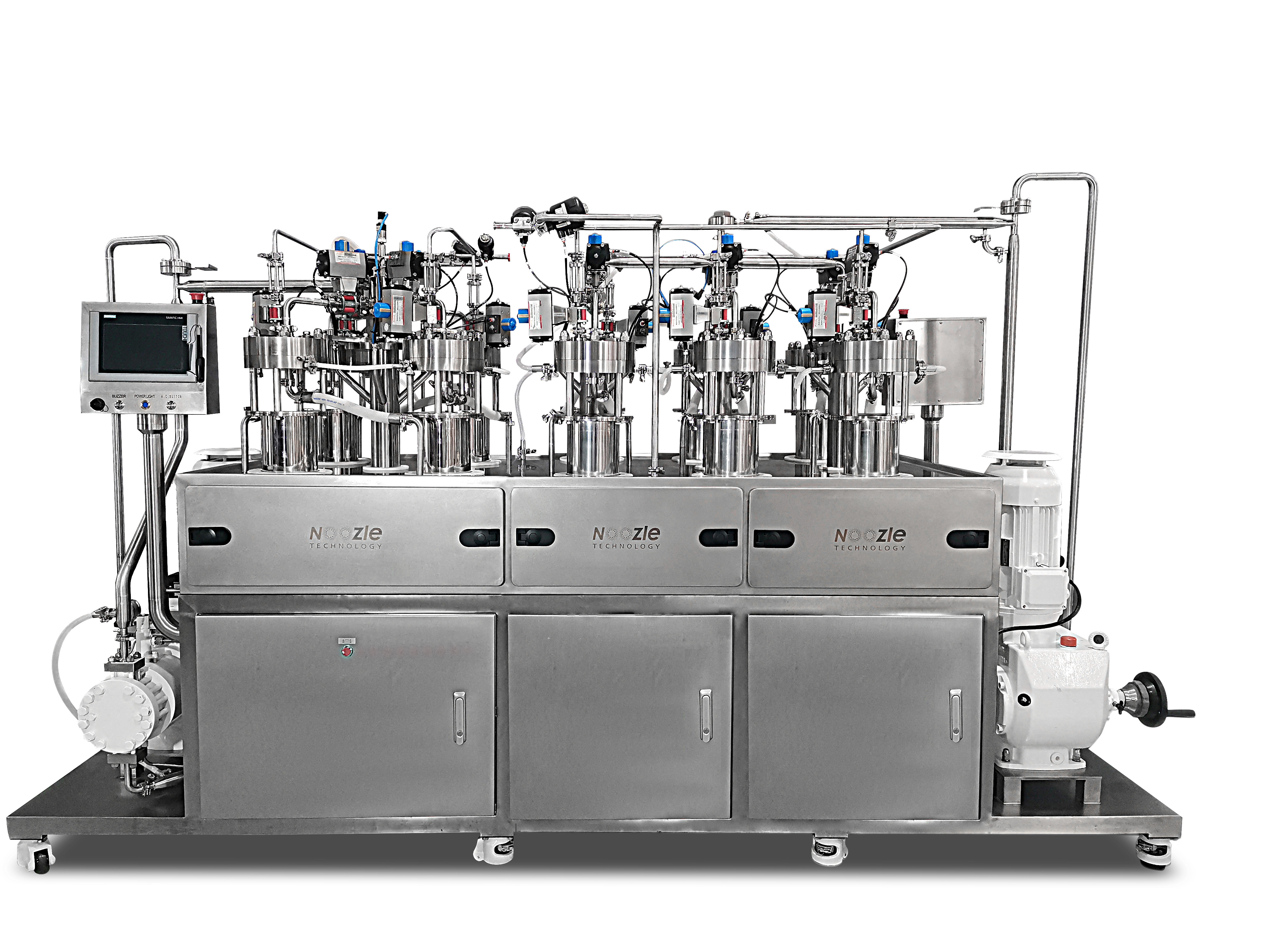
Liposome
Liposome应用简介
Drug delivery systems (the core application)
Tumor therapy: By modifying the surface of liposomes (such as attaching targeting peptides, antibodies, or aptamers), they can specifically recognize receptors on the surface of tumor cells, increase the concentration of drugs at tumor sites, and reduce toxicity to normal tissues. For example, doxorubicin liposomes (Doxil) are used in the treatment of ovarian cancer, breast cancer, etc., and can reduce cardiotoxicity.
Antibacterial and antiviral: Encapsulating antibiotics or antiviral drugs (such as acyclovir) can enhance the accumulation of drugs at infection sites and reduce drug resistance.
Gene therapy: As non-viral vectors, they encapsulate plasmid DNA, siRNA, etc., protect nucleic acids from degradation, and promote their entry into target cells (such as hepatocytes, immune cells), which is used in the treatment of genetic diseases, cancer, etc.
Improving the physicochemical properties of drugs: For poorly soluble drugs (such as paclitaxel), liposomes can improve their solubility and stability; for drugs that are easily enzymatically degraded (such as polypeptides and proteins), liposomes can protect them from damage.
2. Vaccine delivery
Liposomes, as vaccine adjuvants, can encapsulate antigens (proteins, nucleic acids, etc.), promote the uptake by antigen-presenting cells (such as dendritic cells), and enhance immune responses (humoral immunity and cellular immunity). For example, mRNA vaccines (such as COVID-19 mRNA vaccines) often use lipid nanoparticles (LNP, a derivative form of liposomes) to encapsulate mRNA, protecting its stability and promoting intracellular delivery.