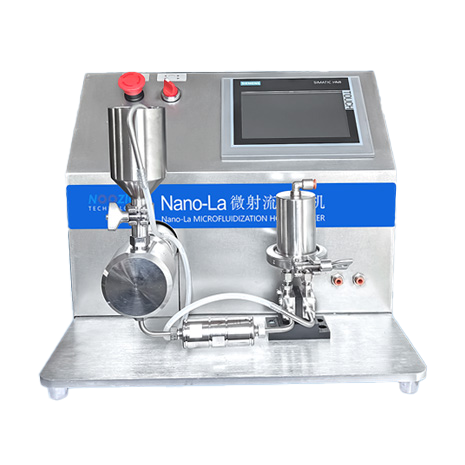
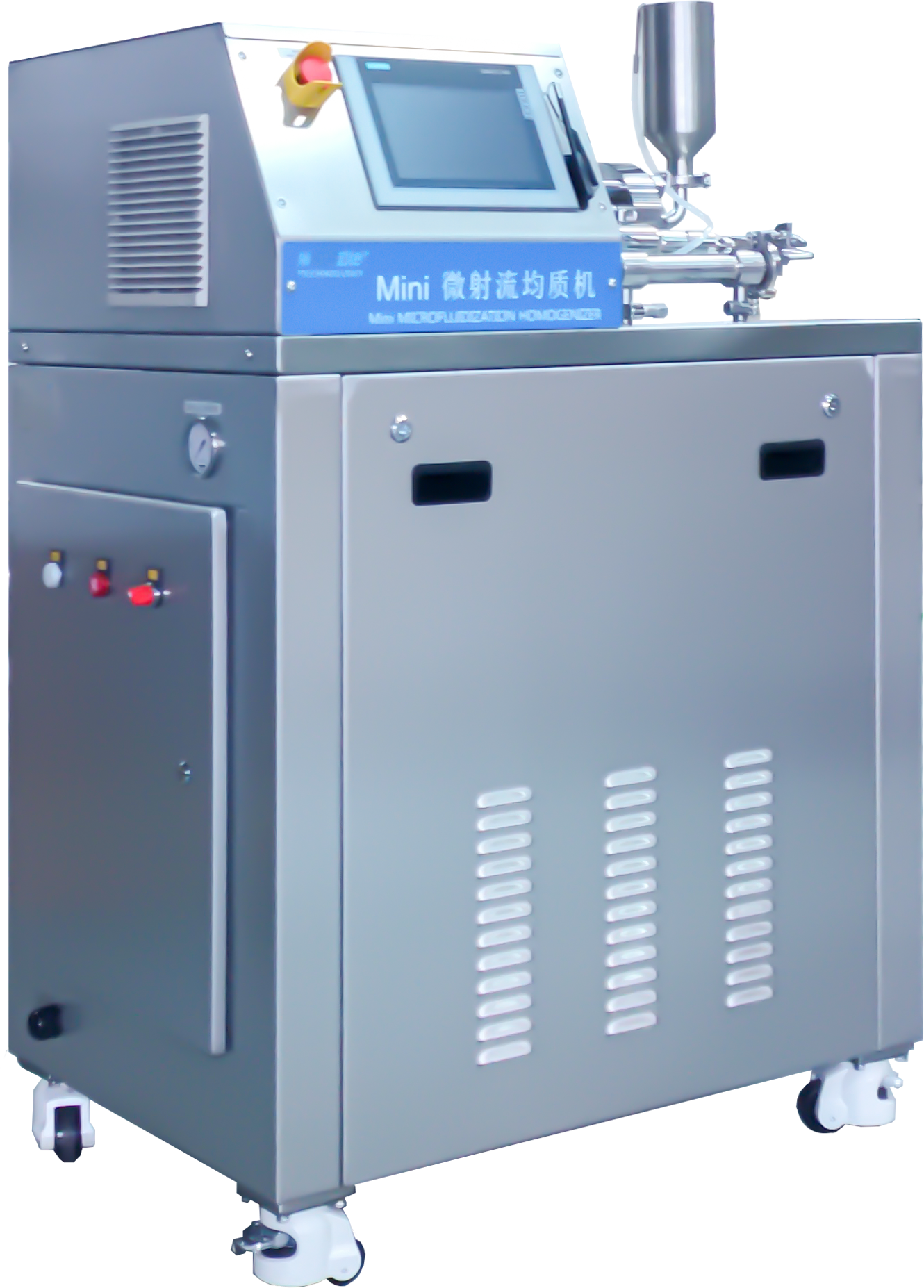
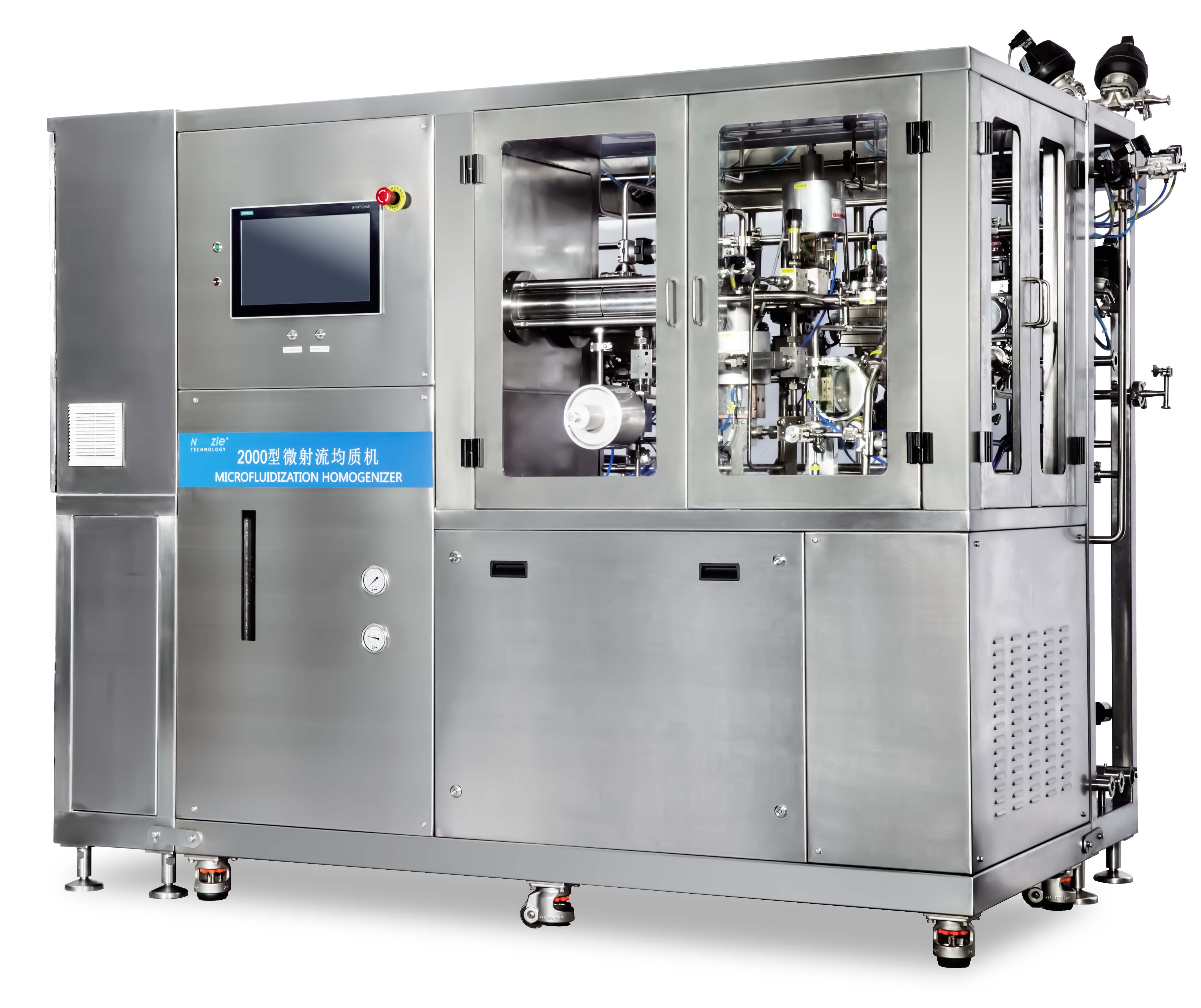
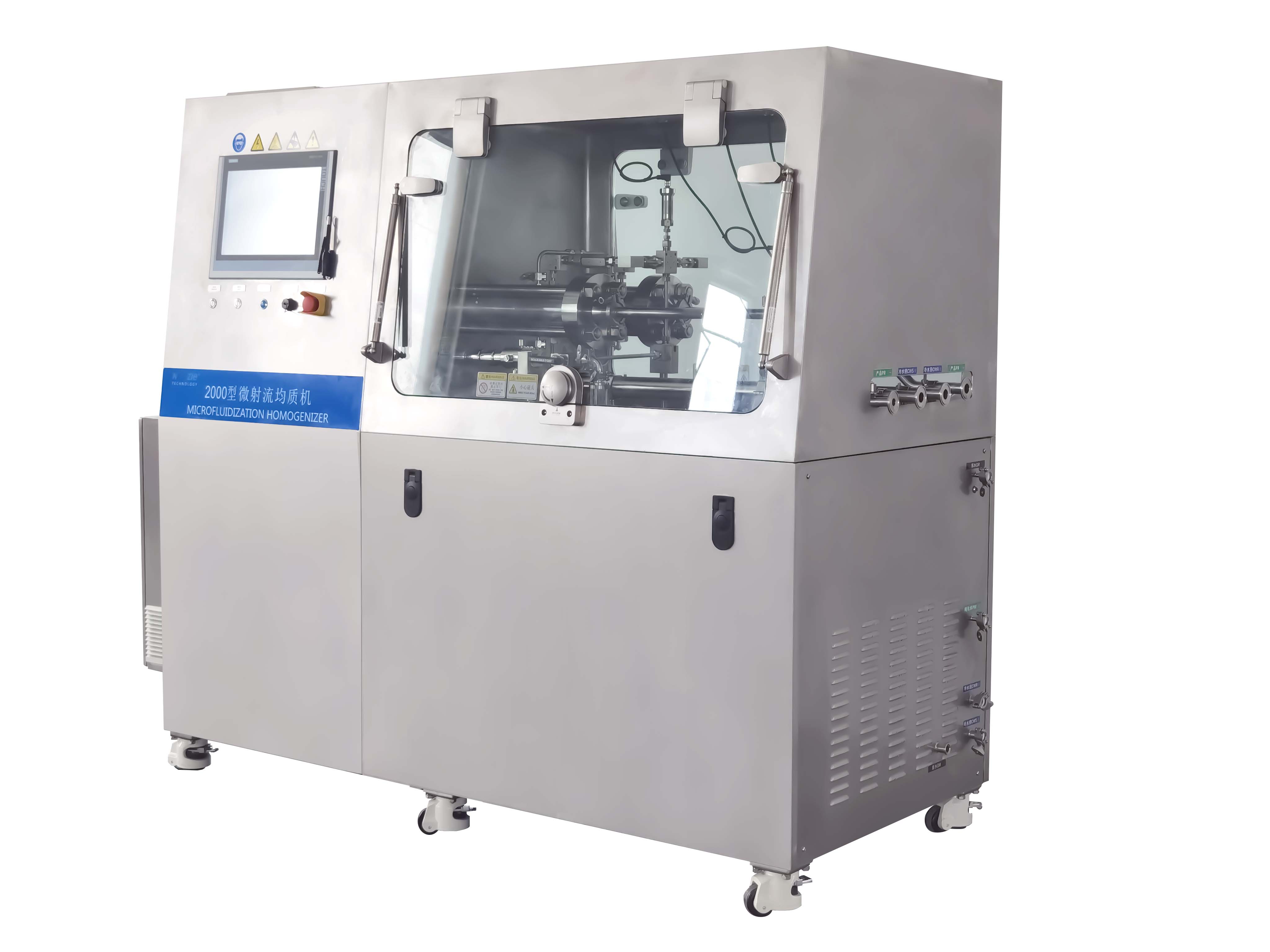
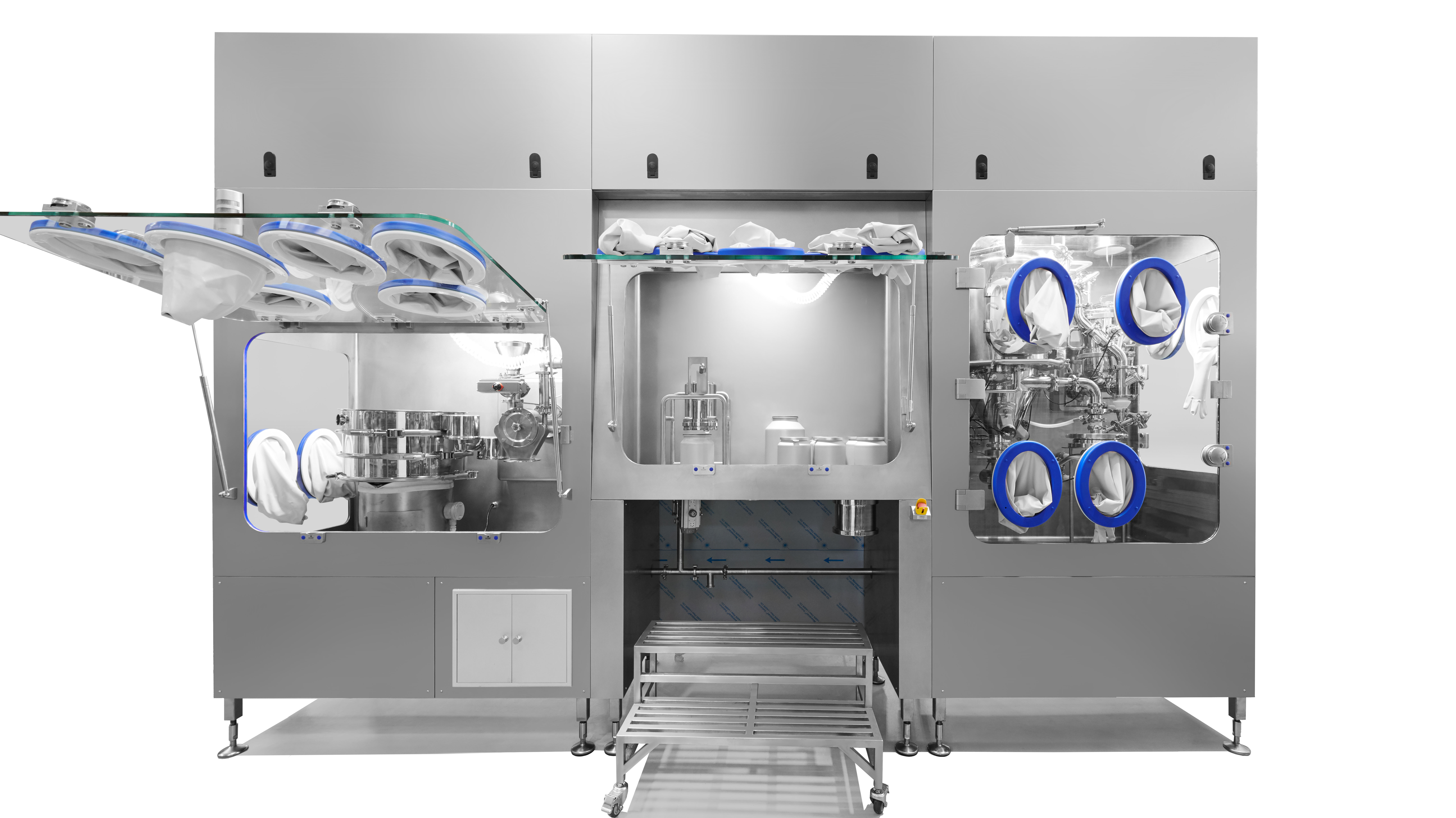
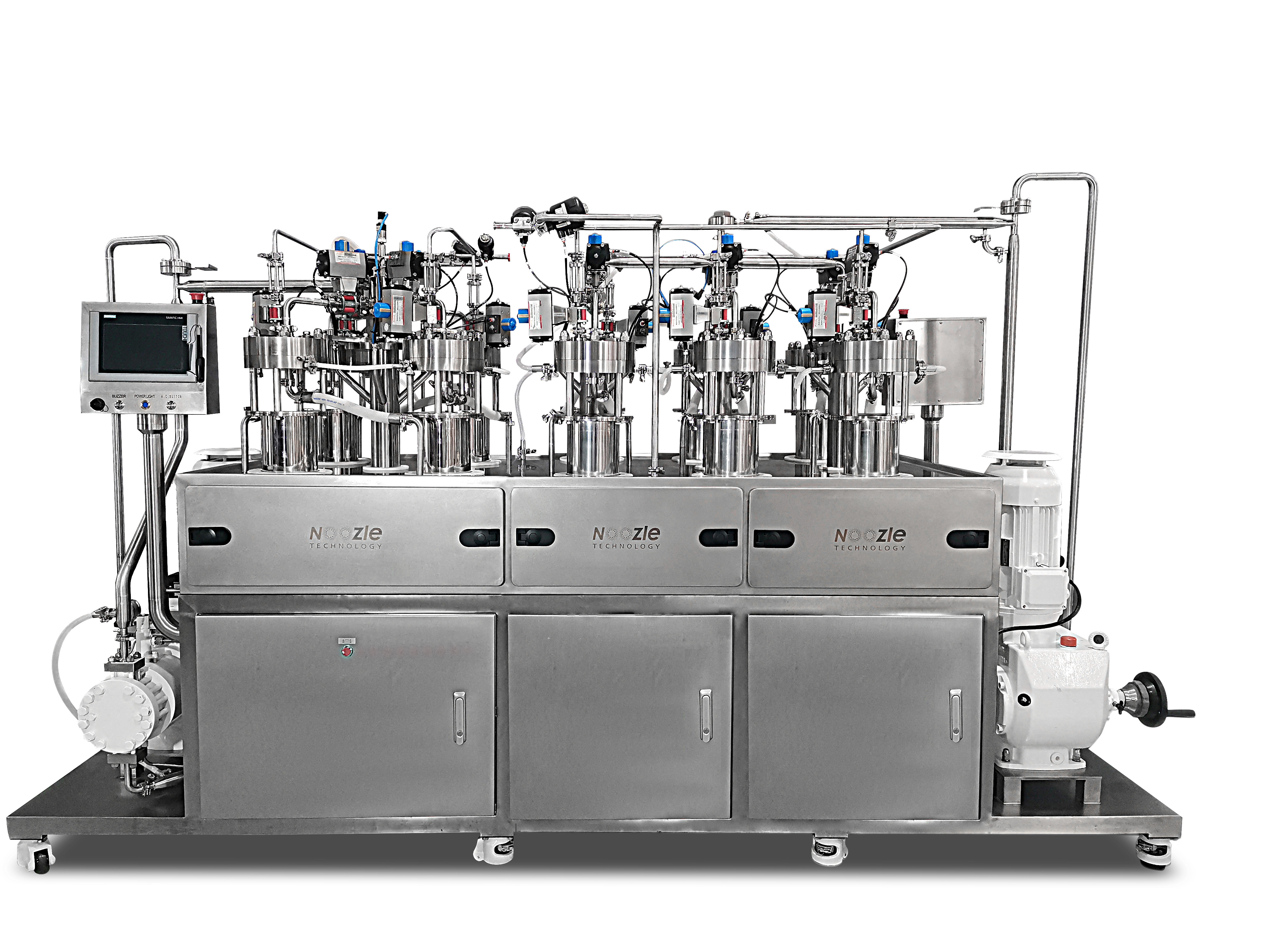
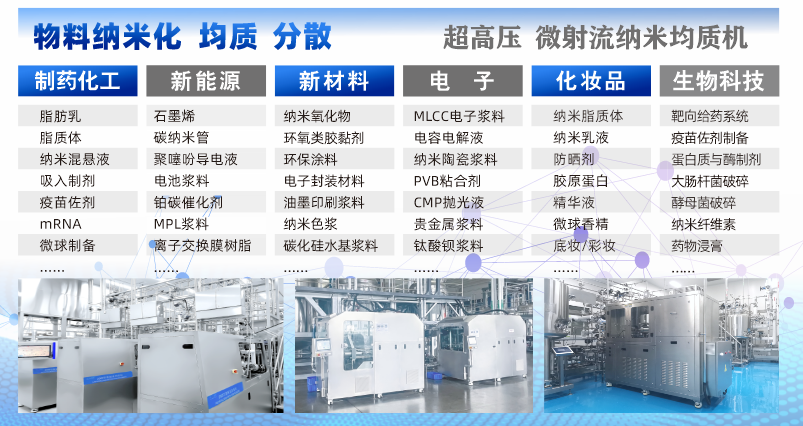
Biotechnology
Biotechnology应用简介
1) Cell disruption and extraction of active substances
Microbial/plant cell disruption: Used for disrupting yeast, Escherichia coli, algae (such as spirulina), and plant cells (such as ginseng, astragalus), to extract intracellular active ingredients like proteins, enzymes, polysaccharides, and pigments.
(2) Preparation of nano-drug formulations
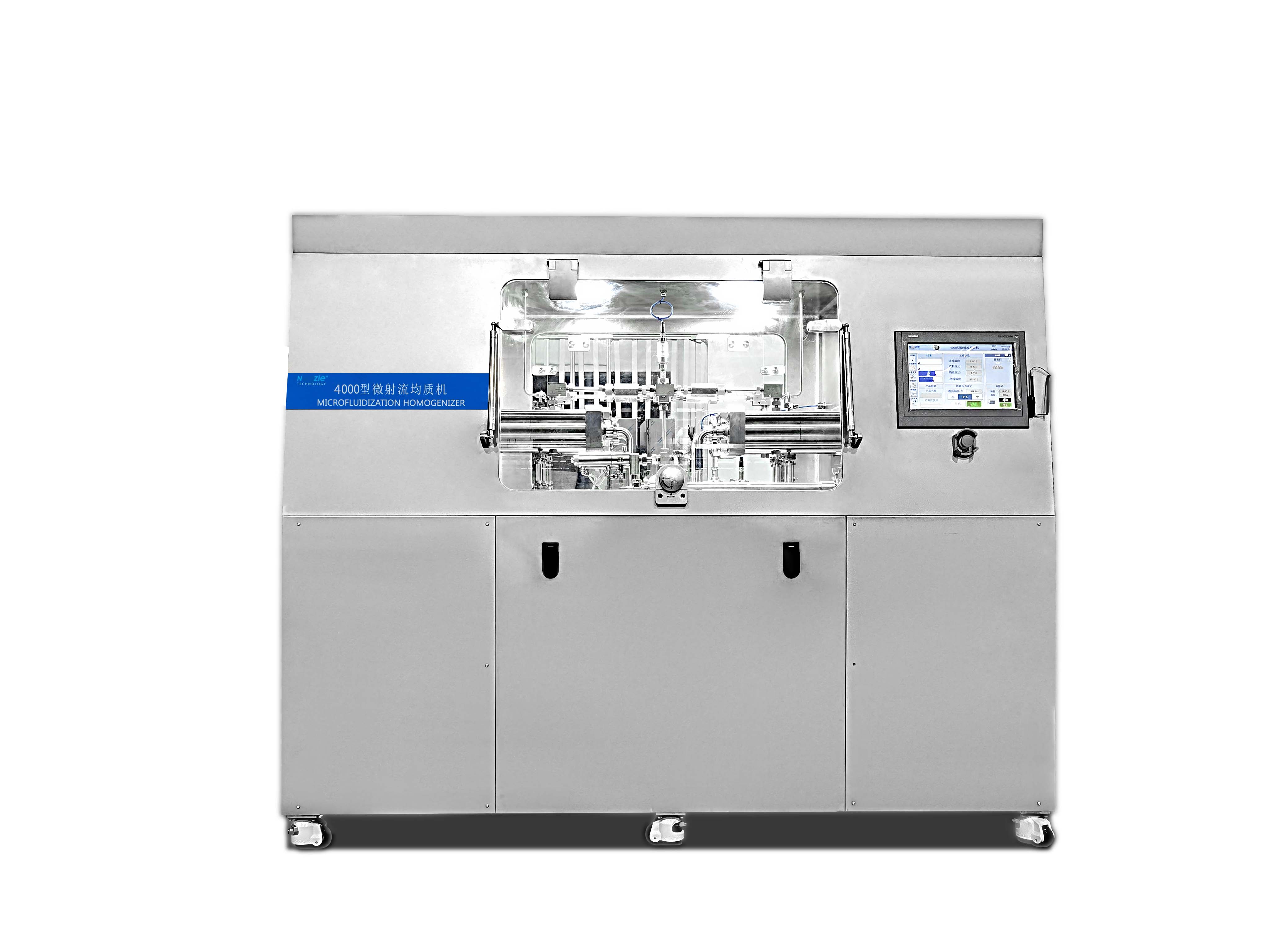
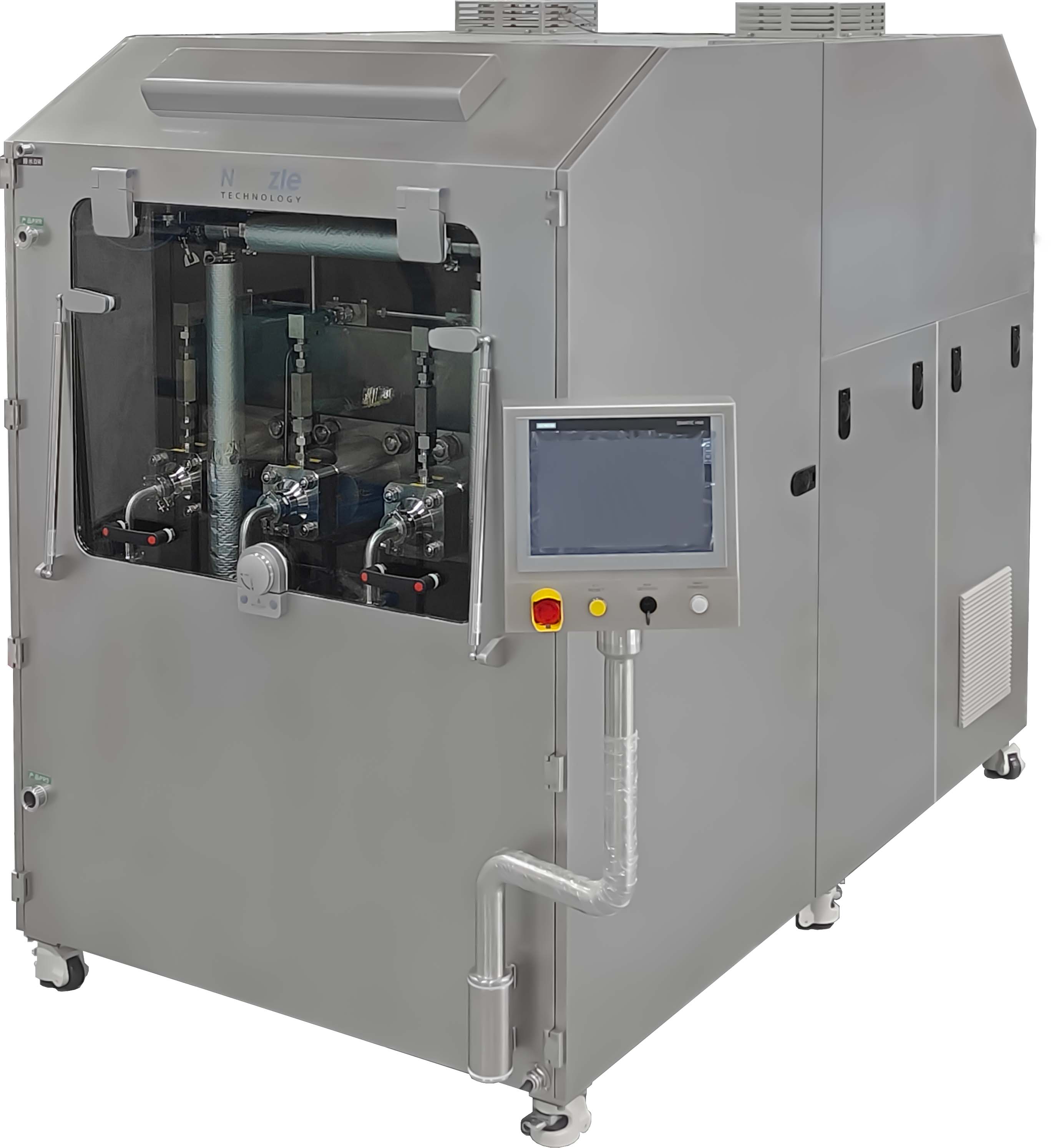
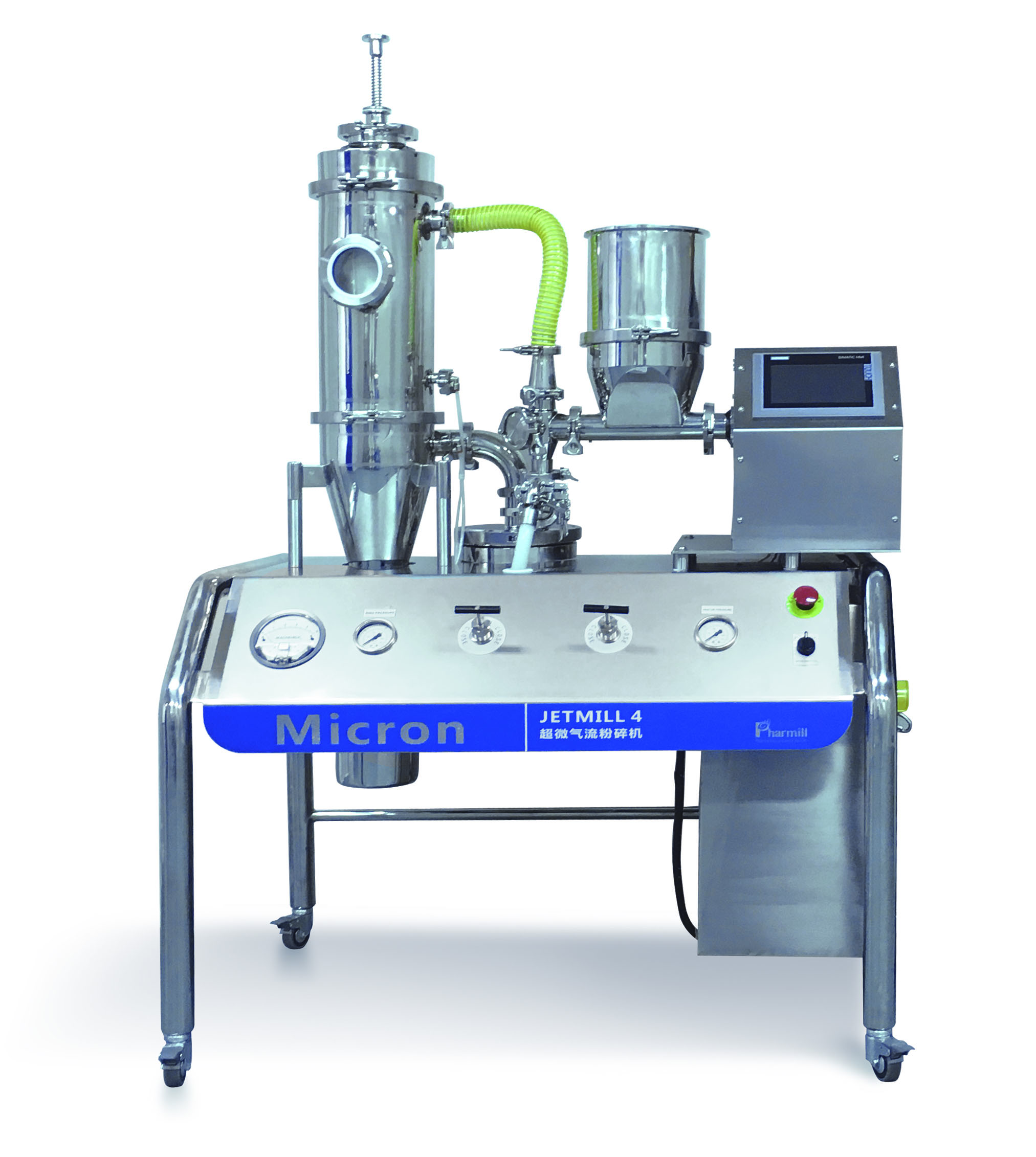
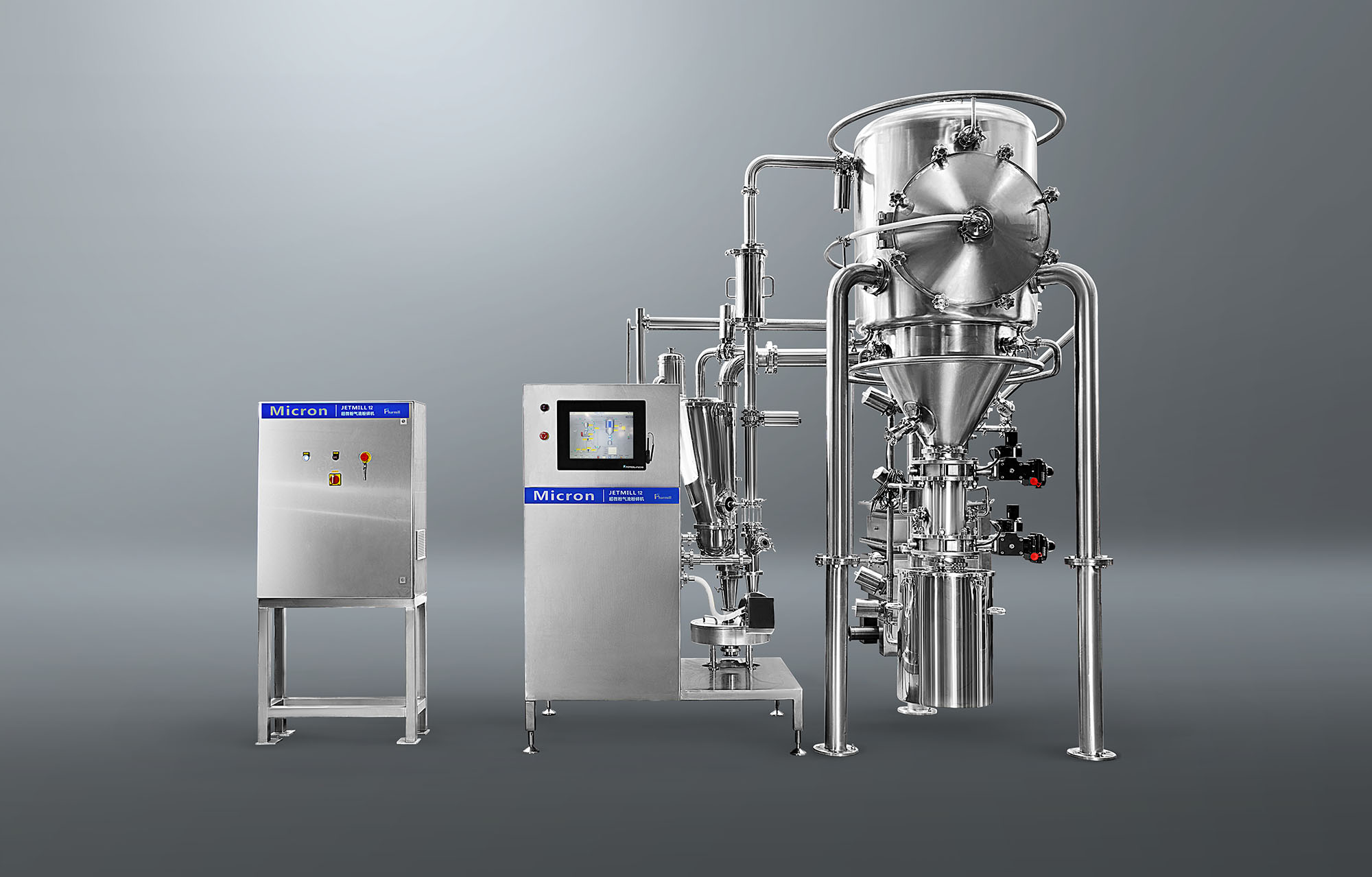
Biotechnology drugs (such as protein drugs, nucleic acid drugs) often need to be made into nano-formulations due to "low solubility, poor bioavailability, and susceptibility to enzymatic degradation", and microfluidic homogenizers are the core preparation equipment:
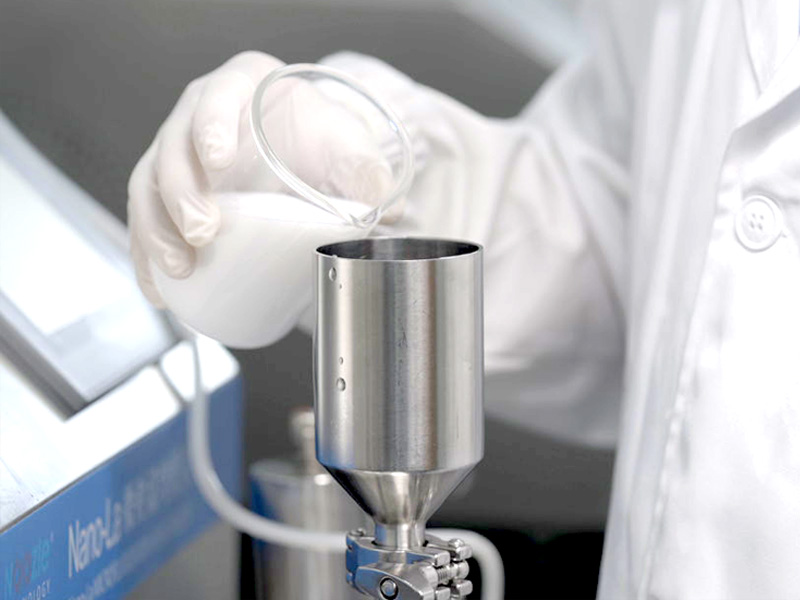
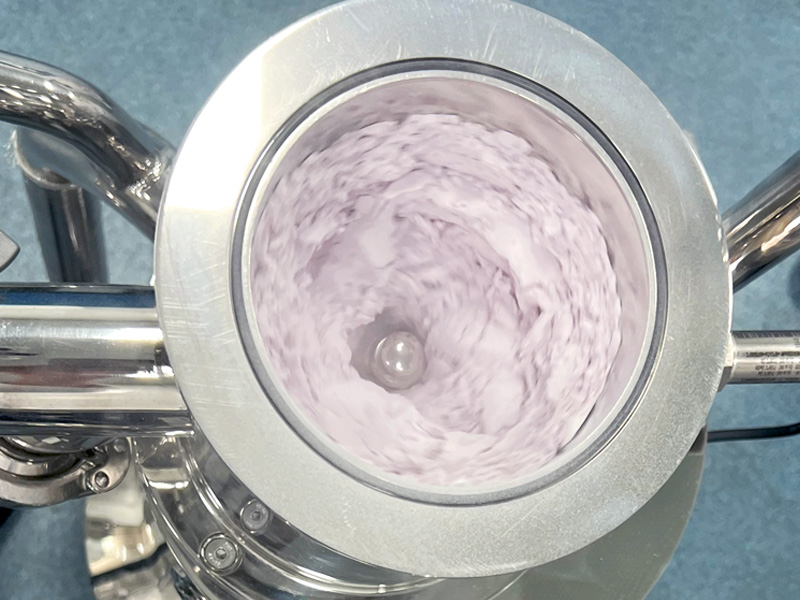
Liposome/nanoemulsion preparation: After mixing lipids (such as phospholipids), drugs (such as siRNA, chemotherapeutic drugs) with the aqueous phase, high-pressure microfluidic treatment is applied to form liposomes or nanoemulsions with uniform particle size (50-200nm), which can improve the water solubility and targeting of drugs (such as targeting tumor cells) and reduce toxic and side effects.
Example: The core carrier of mRNA vaccines, "lipid nanoparticles (LNP)", requires the use of a microfluidic homogenizer to refine components such as lipids and mRNA into particles of about 100nm, ensuring that mRNA is stably encapsulated and can be efficiently taken up by cells.
Nanosuspension preparation: For poorly soluble small molecule drugs (such as some antibiotics, anti-tumor drugs), microfluidics is used to refine drug solid particles to 100-500nm, significantly increasing the specific surface area and improving the dissolution rate and bioavailability of drugs in the intestines.
(3) Dispersion and stabilization of biological macromolecules
Dispersion of proteins/polysaccharides: In the production of recombinant protein drugs (such as monoclonal antibodies) and polysaccharide drugs (such as hyaluronic acid), microfluidics can eliminate protein aggregation (avoiding the formation of precipitates or flocs), improving the stability and storage period of the formulations.